Have you ever felt a sharp, persistent pain in your groin after playing sports or working out? It might not be a regular strain or injury.
You could be dealing with a sports hernia—an often misunderstood condition that can keep you off the field and slow down your progress. Understanding what a sports hernia is, how it happens, and what you can do about it is crucial if you want to stay active and pain-free.
Keep reading to discover everything you need to know to protect your body and get back to the game stronger than ever.

Credit: www.facebook.com
Sports Hernia Overview
A sports hernia is a tricky injury that often confuses athletes and doctors alike. It doesn’t involve a typical hernia bulge, which makes it hard to spot. Yet, it causes intense groin pain that can sideline you from your favorite sport or workout.
Understanding what a sports hernia really is can help you catch it early and avoid worsening the injury. It mostly affects athletes involved in sports requiring sudden twisting or turning movements, like soccer, hockey, or football.
Have you ever felt a sharp, persistent pain in your groin after a hard play? That could be a sign you’re dealing with a sports hernia.
What Exactly Is A Sports Hernia?
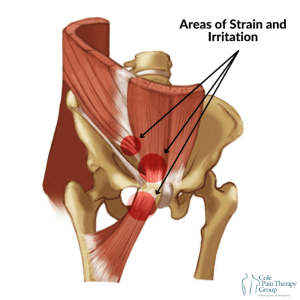
A sports hernia, also called athletic pubalgia, is a tear or strain of the soft tissues in your lower abdomen or groin. Unlike a traditional hernia, there’s no visible lump. Instead, the injury affects muscles, tendons, or ligaments around the groin area.
This injury happens from repetitive stress or sudden twisting motions that put pressure on your pelvic region. Because there’s no obvious bulge, it’s often misdiagnosed or overlooked, leading to prolonged pain and frustration.
Who Is Most At Risk?
Sports hernias are common among athletes who play high-intensity sports with lots of running, cutting, and twisting. Soccer players, hockey players, and football athletes report these injuries more than others.
- People who train intensely without enough rest
- Those with weak core muscles or imbalanced strength between legs
- Athletes who suddenly increase their activity level
Think about your training habits—are you pushing too hard without proper recovery? That could increase your risk.
Symptoms To Watch For
Pinpointing a sports hernia can be challenging because symptoms overlap with other groin injuries. The most common signs include:
- Sharp or burning pain in the groin during activity
- Pain that improves with rest but returns when you move
- Discomfort when coughing, sneezing, or twisting
If you’re constantly nursing a nagging groin pain that won’t quit, getting a professional evaluation is key. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to longer recovery times and more serious damage.

Credit: www.facebook.com
Causes Of Sports Hernia
Sports hernia happens because of stress or injury to the groin area. It affects athletes and active people. Understanding what causes sports hernia helps in prevention and treatment. The causes mostly relate to physical strain and specific activities.
Physical Strain Factors
Repeated stress on the lower abdomen and groin weakens muscles and tendons. Sudden twisting or turning increases the risk of injury. Weak core muscles fail to support the groin properly. Overuse of muscles during training or competition causes tiny tears. Imbalance between strong thigh muscles and weaker abdominal muscles adds strain.
Common Activities Leading To Injury
- Running fast or sprinting with quick direction changes
- Kicking in sports like soccer or football
- Sudden twisting motions in hockey or basketball
- Heavy lifting or intense weight training
- Jumping and landing awkwardly in sports like volleyball
These activities put extra pressure on the groin. Over time, they may cause a sports hernia. Awareness of these causes helps athletes avoid injury and stay active.
Symptoms Of Sports Hernia
Recognizing the symptoms of a sports hernia early can make a huge difference in your recovery. These symptoms can be tricky because they often mimic other injuries, especially in athletes who push their bodies hard. Understanding what to look for helps you get the right treatment and avoid worsening the injury.
Initial Signs And Indicators
The first sign of a sports hernia is usually a sharp pain in the groin area during physical activity. You might notice discomfort when twisting, turning, or sprinting. This pain often feels deep and persistent rather than sharp and sudden.
Along with pain, some people experience tenderness around the lower abdomen or upper thigh. You may also feel stiffness or weakness in your groin muscles, which can impact your ability to perform at your best. If you’ve ever felt a dull ache that won’t go away after exercise, this could be a warning sign.
Differentiating From Other Conditions
Sports hernia symptoms overlap with other common injuries like groin strains or hip flexor pulls, making diagnosis confusing. Unlike a simple muscle strain, a sports hernia pain usually worsens with specific movements such as sudden direction changes or intense twisting.
Unlike a traditional hernia, you won’t see a visible bulge with a sports hernia. This absence often leads to misdiagnosis, so don’t ignore persistent groin pain even if there’s no obvious lump. If rest and basic treatment don’t ease your symptoms, it’s time to consult a specialist who can use imaging tests to pinpoint the problem.
Diagnosis Methods
Diagnosing a sports hernia can be tricky because its symptoms often mimic other groin injuries. Accurate diagnosis is essential to get the right treatment and avoid prolonging pain or discomfort. Let’s look at how doctors pinpoint a sports hernia through various examination techniques and diagnostic tests.
Clinical Examination Techniques
Your doctor will start with a thorough physical exam, focusing on the area around your groin and lower abdomen. They will check for tenderness, swelling, or any unusual bulges by gently pressing different spots. You might be asked to perform specific movements or stretches that could trigger your pain, helping to reveal the exact source of the problem.
Doctors often observe your posture and how you walk or run during the exam. This can highlight muscle imbalances or weaknesses contributing to your injury. Have you noticed how pain changes with certain activities? Sharing these details can help your doctor make a sharper diagnosis.
Imaging And Diagnostic Tests
Since a sports hernia won’t always show up on basic scans, your doctor might order advanced imaging tests. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is commonly used because it shows soft tissues clearly, helping spot muscle tears or inflammation. Sometimes an ultrasound is done to check for abnormalities in the groin area while you move or strain.
In some cases, doctors use diagnostic injections to confirm the pain source. They inject a small amount of anesthetic near the suspected injury spot. If the pain disappears temporarily, it confirms the diagnosis of a sports hernia.
Have you ever experienced frustration when tests come back normal but pain persists? Understanding the variety of diagnostic tools available can give you confidence in getting the right treatment path.
Effective Treatment Options
Treating a sports hernia requires careful attention to reduce pain and restore strength. Many options exist to help athletes return to their activities quickly and safely. Treatments focus on healing the injury and improving muscle balance around the affected area.
Choosing the right treatment depends on the injury’s severity and how the body responds. Starting with less invasive methods is common. If these do not work, surgical options may become necessary. Understanding both approaches helps in making informed decisions for recovery.
Non-surgical Approaches
- Rest and avoid activities that cause pain.
- Physical therapy to strengthen core and hip muscles.
- Use of ice packs to reduce inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory medications to ease discomfort.
- Gradual return to sports under professional guidance.
Surgical Interventions
- Repair of torn muscles or tissues in the groin area.
- Minimally invasive techniques like laparoscopy.
- Removal of any damaged tissue causing pain.
- Post-surgery physical therapy to regain strength.
- Faster recovery for severe or persistent cases.

Credit: www.facebook.com
Recovery And Rehabilitation
Recovering from a sports hernia takes patience and a clear plan. Your body needs time to heal, and rushing can cause setbacks. Understanding what comes after treatment helps you get back in the game stronger and smarter.
Post-treatment Care
Right after treatment, whether surgery or conservative care, rest is crucial. Avoid any activities that put strain on your groin area for at least a few weeks. You may feel tempted to push through pain, but that only delays healing.
Managing pain and swelling with ice packs and prescribed medications is part of your daily routine. Keep an eye on your symptoms—if pain worsens or mobility decreases, contact your doctor immediately.
Simple lifestyle adjustments, like sleeping positions and avoiding heavy lifting, can make a big difference during recovery. Are you prepared to change your habits temporarily to support your healing?
Physical Therapy Recommendations
Physical therapy is your roadmap back to full strength. A skilled therapist will guide you through exercises that target core and pelvic muscles, areas often weakened by sports hernias.
Therapy starts gently, focusing on improving flexibility and reducing pain. As you progress, exercises become more dynamic, preparing you for the demands of your sport.
- Core stabilization moves to support the pelvis
- Hip strengthening exercises to balance muscle groups
- Gradual reintroduction of sport-specific drills
Consistency is key. Missing sessions or skipping exercises can slow recovery. Have you set a schedule to stay committed to your therapy?
Remember, your goal is not just to heal but to prevent future injuries. Working closely with your therapist ensures you build resilience, not just recovery.
Preventing Sports Hernia
Preventing a sports hernia is important for athletes and active people. It helps avoid pain and long recovery times. Focusing on muscle strength and smart training keeps the body balanced and less prone to injury. Simple changes and exercises can make a big difference.
Strengthening Exercises
Strong muscles around the hips and lower abdomen reduce stress on the groin. Exercises should target the core, hip flexors, and adductors. Examples include:
- Planks to build core stability
- Leg raises to strengthen hip flexors
- Side lunges to work on inner thigh muscles
- Bridges to activate glute muscles
Regular stretching helps keep muscles flexible and less likely to tear.
Lifestyle And Training Modifications
Proper warm-up routines prepare muscles for intense activity. Gradually increasing training intensity prevents overload. Avoid sudden bursts of high effort without conditioning. Rest days allow muscles to recover and heal. Wearing supportive gear may help reduce strain. Eating a balanced diet fuels muscle repair and strength.
Impact On Athletic Performance
A sports hernia can greatly affect an athlete’s ability to perform. This injury causes pain and weakness in the groin area. Athletes may find it hard to run, twist, or kick. The impact varies from short-term discomfort to long-lasting issues. Understanding these effects helps athletes manage recovery and maintain their performance.
Short-term Effects
In the early stages, a sports hernia causes sharp groin pain. Sudden movements may trigger discomfort or sharp stabs. This pain limits speed and agility. Athletes often reduce training intensity to avoid worsening the injury.
Other short-term effects include:
- Reduced flexibility
- Decreased muscle strength
- Difficulty changing directions quickly
- Lower endurance during workouts
These factors can cause a drop in overall performance. Rest and proper treatment are critical during this phase.
Long-term Considerations
If untreated, a sports hernia can cause lasting damage. Chronic pain may develop, interfering with daily activities. Athletes risk compensating with other muscles, leading to further injuries.
Long-term issues include:
- Persistent groin pain
- Reduced range of motion
- Weakness affecting balance and coordination
- Possible need for surgery
Ongoing physical therapy can help regain strength and prevent relapse. Ignoring symptoms can end an athlete’s career prematurely.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Exactly Is A Sports Hernia?
A sports hernia is a painful soft tissue injury in the groin area. It occurs from intense sports activities causing strain or tears in the muscles or tendons.
What Are Common Symptoms Of A Sports Hernia?
Symptoms include sharp groin pain, especially during physical activity. Pain worsens with twisting, turning, or sudden movements and improves with rest.
How Is A Sports Hernia Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves physical exams and imaging tests like MRI. Doctors assess pain location, muscle weakness, and rule out other injuries.
What Treatments Are Effective For Sports Hernias?
Treatment includes rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and sometimes surgery. Early care helps reduce pain and speeds recovery.
Conclusion
A sports hernia causes pain in the groin during physical activities. It often affects athletes and active people. Early diagnosis helps prevent serious injury. Treatment usually includes rest, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery. Understanding symptoms can lead to quicker recovery.
Stay aware of your body’s signals to avoid worsening pain. Proper care helps you return to sports safely. Keep your muscles strong and flexible to reduce risk. Taking action early makes a big difference in healing.